How to build a Network from scratch
Networking & Communications Course
If you are interested taking Networking & Communications Course then get in touch using the contact us form or you can directly email us at info.cyberworldacademy@gmail.com or use the phone numbers to contact us. Call Now (+91) 9081006788
It is the interconnection of multiple devices, generally termed as Hosts connected using multiple paths for the purpose of sending/receiving data or media.
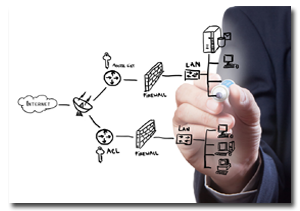
There are also multiple devices or mediums which helps in the communication between two different devices which are known as Network devices. Ex: Router, Switch, Hub, Bridge
How networking works, and how to use different devices to build networks. Computer networking has existed for many years, and as time has passed the technologies have become faster and less expensive. Networks are made up of various devicesócomputers, switches, routersóconnected together by cables or wireless signals. Understanding the basics of how networks are put together is an important step in building a wireless network in a community or neighborhood.
Rs. 12,000/- Duration: 50 Days
[Note: Prices displayed are after Discount and includes GST]Detailed Syllabus of Networking & Communications Course:
|
|
|

